
ML for CO 综述
Yoshua Bengio, Andrea Lodi, and Antoine Prouvost. "Machine learning for combinatorial optimization: A methodological tour d'horizon", European Journal of Operational Research 290.2 (2021): 405-421.
不失一般性的,CO 问题可以被公式化为一个受约束的最小优化问题。如果目标和约束是线性的,则该问题称为线性规划(LP)问题。如果一些变量也被限制为只能为整数值,则问题被称为混合整数线性规划(MILP)问题。可用单纯形算法多项式复杂度求解 LP 问题。
分支限界(branch and bound),分支是使用广度优先策略,依次生成扩展结点的所有分支,限界是在结点扩展过程中,计算结点的上界,搜索的同时剪掉某些分支。分支限界法就是把问题的可行解展开,再由各个分支寻找最佳解。
对于 MILP 问题,分支限界算法为将问题松弛为实数变量后分解为小问题。
End to end learning
通过 ML,由 Problem defifinition 直接得到 Solution。ML 适合在较短的计算时间内获得准确的解决方案,因为一些复杂性是在学习阶段离线解决的。
Learning meaningful properties of optimization problems
通过 ML,为传统的运筹优化方法提供信息。
Machine learning alongside optimization algorithms
构建 CO 算法,在整个执行过程中反复调用 ML 模型。主算法控制高级结构,同时经常调用ML模型以协助较低级别决策。
最大公共子图(MCS)
Ciaran McCreesh, Patrick Prosser, and James Trimble. "A Partitioning Algorithm for Maximum Common Subgraph Problems.", International Joint Conference on Artificial Intelligence (2017): 712-719.
Yanli Liu, Chumin Li, Hua Jiang, and Kun He. "A Learning Based Branch And Bound For Maximum Common Subgraph Related Problems", AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence 34. (2020): 2392-2399.
Jianrong Zhou, Kun He, Jiongzhi Zheng, Chu-Min Li, and Yanli Liu. "A Strengthened Branch and Bound Algorithm for the Maximum Common (Connected) Subgraph Problem", European Conference on Artificial Intelligence (2022): 1908-1914.
The McSplit Algorithm
搜索过程中的当前状态为点对的映射
当前状态对应的答案上界为:
McSplit+RL
因为预计的上界越小,越可能剪枝,因此考虑将上界的减少量作为奖励。
同时,若考虑上界的减少率,则又得到一种变体方法。
考虑点对的匹配作为奖励。
McSplit+LL Algorithm
Long-Short Memory (LSM)
随着搜索的深入,当前状态会有很大的变化,均匀地累积分数会导致由大部分历史评估值引起的偏差。因此,需要一种能够消除历史评估的影响的机制。
考虑短期阈值
Leaf vertex Union Match (LUM)
叶节点定义为只跟一个点相邻的节点。一个点的叶子定义为与该点相邻的叶节点。
定理:在进行
旅行商问题(TSP)
LKH
求解 TSP 的启发式算法可分为三类:回路构造算法、回路改进算法和复合算法。复合算法通常使用回路改进算法对回路构造算法得到的初始解进行改进。LKH 算法是一种利用 k-opt 来改进启发式构造的初始行程的复合算法。
k-opt:替换当前解的
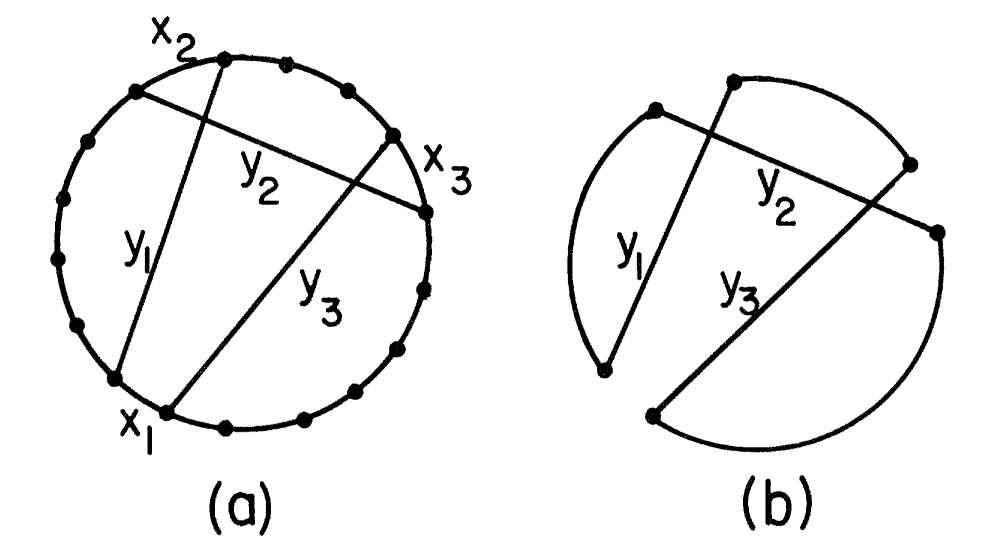
1-tree 下界:从
定义
Held-Karp 下界:LKH 算法通过添加惩罚
VSR-LKH
Jiongzhi Zheng, Kun He, Jianrong Zhou, Yan Jin, and Chu-min Li. "Combining Reinforcement Learning With Lin-Kernighan-Helsgaun Algorithm For The Traveling Salesman Problem", AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence 35 (2021): 12445-12452.
VSR-LKH 中,k-opt
过程不再是遍历候选边集,而是通过强化学习来从候选边集选择添加的边。对于该强化学习,状态为当前需要加边的点,动作为加边,加边后状态转移为所加边的另一个端点,奖励为:
NeuroLKH
Liang Xin, Wen Song, Zhiguang Cao, and Jie Zhang. "NeuroLKH: Combining Deep Learning Model with Lin-Kernighan-Helsgaun Heuristic for Solving the Traveling Salesman Problem.", Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems (2021): 7472-7483.
LKH 中迭代
首先将原图转化为稀疏有向图
用稀疏图网络来预测边的权值
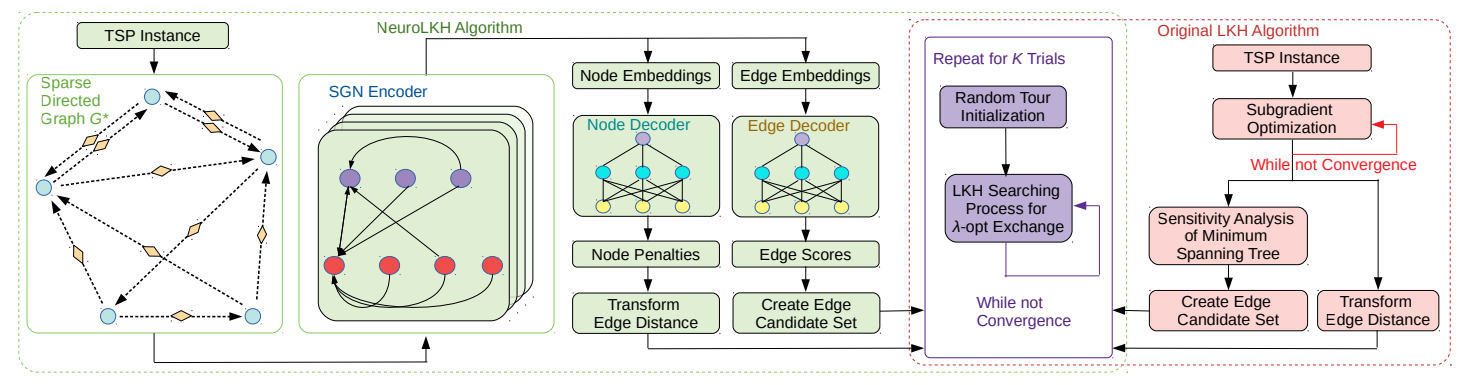
先将边和点的信息转化为特征向量,维度为
边的权值
对于大规模的数据,边的权值
图匹配
Junchi Yan, Shuang Yang, and Edwin R. Hancock. "Learning for Graph Matching and Related Combinatorial Optimization Problems.", International Joint Conference on Artificial Intelligence 5 (2020): 4988-4996.